Curtain Wall Vs Cladding Panels: What’s the Difference?
Which One to Choose?
While considering the infill of a building, two major selections often arise: cladding panels and curtain walls. Both systems emphasize the architectural appearance of a building but have entirely different functions and come with separate technical and visual features. Knowing the differences will enable you to adequately pick a system suited for your project’s needs. In this article, we explore the curtain wall vs cladding panels: what’s the difference? Looking into their functions, components, installation procedures, performance criteria, associated expenses, latest advancements, as well as industry standards to guide architects, constructors, and even homeowners towards better choices.
What is a Curtain Wall?
A curtain wall is defined as an outer covering that protects parts of buildings without adding weight to the structure's frame; it is glazed with aluminum and further stone or metal panels. As opposed to load-bearing walls, curtain walls do not support any portion of building weight other than their mass shell thin skin detached from internal supports.
Key Features of Curtain Walls:
• They are mounted vertically along each section of the building's skeleton beams, onto which the structure hangs a suspended steel or concrete frame that shall transmit.
• They enhance modern aesthetics alongside offering daylight penetration through tear-resistant, regularly opening glass vessels, sealing ki send mark long taste magnetic bubble.
• Unitized or stick-built systems: These can be prefabricated into sections (unitized) or constructed on-site piece by piece (stick-built).
• High performance: These are built to maintain an enclosure’s airtightness, watertightness, and thermal insulation properties as well as resist wind loads and seismic activity.
• Common in commercial and high-rise buildings: These are often associated with skyscrapers and office towers.
What are Cladding Panels?
These are secondary outer materials attached to the structural frame of a wall or building. Cladding serves dual purposes as a protective layer that shields the building from weather elements while also enhancing its aesthetics.
Key Features of Cladding Panels:
• Can be structural or non-structural: Certain cladding panels may carry light loads, but most attach directly to the building's envelope.
• The range is quite extensive: Wood, aluminum, steel, fiber cement, brick, stone, composite panels, vinyl, and more.
• Typically opaque: Unlike curtain walls, cladding panels predominantly block light, though they may have windows or perforations.
• Methods of installation: Sections can be pre-fabricated and then fastened either mechanically or adhesively to walls.
• Flexible applications: Used across all types of residential structures, down to commercial and industrial buildings for facade design, along with protection.
Structural Differences: Load-Bearing Vs Non-Load-Bearing
Curtain Wall vs Cladding Panels: What’s the Difference? The distinction between curtain walls and cladding panels is most noticeable in their construction function stems from structural differences.
• Curtain Wall: These elements are completely non-load-bearing. A curtain wall hangs from the building's structural frame and only supports its weight, along with wind pressure.
• Cladding Panels: Cladding panels are either semi-structural or non-load-bearing bearing depending on the design specified. Cladding can provide some load support or act as a rainscreen, but is secondary to the building frame or walls, which contain the primary structural loads.
Because curtain walls do not bear loads, there is greater freedom for large window spans and slender framing, giving ease to architects. On the other hand, cladding serves mainly a protective function, concentrating on insulation, including thermal insulation and weatherproofing.
Curtain Wall Materials:
• Aluminum frames: Widely used due to being lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to fabricate, while maintaining structural integrity.
• Glass: Utilized in the form of insulated glass units (IGUs) featuring coatings that control solar energy as well as thermally insulate.
• Spandrel panels: Opaque panels utilized for concealing structural elements or mechanical spaces.
• Composite materials: Used sometimes due to improvement in aesthetic appeal or performance grade.
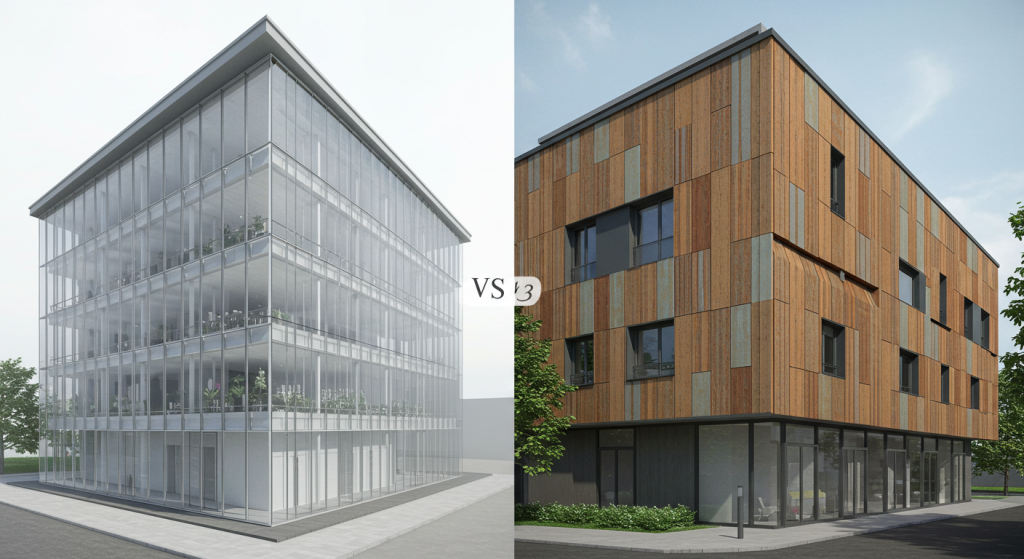

Cladding Panel Materials:
• Wood: Provides a natural warm texture indoors comes with maintenance issues such as rot and weathering.
• Metal (Aluminum, Steel, Copper): Preferred metals for modern structures are durable, having sleek exteriors.
• Fiber Cement: Strong resistance against fire, while being low-maintenance, makes this material durable.
• Stone & Brick: Outstanding durability along with traditional and timeless aesthetics.
• Vinyl & Composite Panels: Diverse finishes alongside lightweight materials make these very economical.
Installation & Fabrication Differences
Curtain Wall Installation:
- Unitized Curtain Wall Systems: Large panels assembled off-site into pre-fabricated portions and then affixed to the building facade. More efficient pacing, greater oversight during manufacturing, but fewer customization options.
- Stick-Built Curtain Walls: Components (frames, glass, spandrel panels) are put together on location, which increases the time needed for completion, but offers more adaptable construction options.
- Complexity: Designed precision is crucial due to factors like thermal expansion and structural shifts alongside seal-tight water resistance.
Cladding Panel Installation:
- Prefabricated Panels: Arrive ready for mounting onto support rails or direct attachment to the building envelope.
- On-site Fabrication: Units like stone and brick may need more conventional assembly through masonry techniques.
- Faster & Simpler: Compared to curtain walls, cladding installation, especially for low-rise buildings, tends to be quicker and simpler than framework assembly.
Performance & Energy Efficiency
Curtain walls have distinct advantages when it comes to cutting-edge technology in performance metrics like energy efficiency and spacing structure digitizes-reducing thermal movements considerations along with glass penetration effectiveness over other framed walls or clad panel counterparts.
Natural views combined with ventilation windows offer optimized lighting while providing unobscured panoramic vistas, enhancing visually captivating spaces artfully designed within architectural brilliance seamlessly integrated into dynamic landscapes
• Incorporate thermal breaks in aluminum frames to mitigate heat transfer.
• Energy-efficient glazing features low emissivity glass (low E).
• Can add ventilated or double skin facades for improved climate control.
• Require precise waterproofing and air sealing to eliminate leaks or drafts.
Cladding Panel Performance:
• Temperature-controlled environments often improve moisture insulation and infiltration protection.
• Vapor barriers can be integrated behind the panels for increased weatherproofing.
• Rainscreen cladding systems provide ventilated facades that effectively manage moisture, improving drainage performance.
• Fiber cement and metal panel materials are durable with low maintenance requirements.
• Commonly designed to be more opaque, which helps reduce incoming daylight, therefore improving thermal performance.
System Selection: Applications for Curtain Walls and Cladding Panels
Ideal Uses for Curtain Walls Include:
• In high-rise commercial buildings where aesthetics and daylighting hold significant value
• Modern projects that require a sleek glass facade
• End-of-the-line high-performance envelopes needing air control/thermals for the building
• In case non-load-bearing structure design versatility is needed
Conclusion
It is important to note that both curtain walls and cladding panels are distinct in their own way to allow selection of a suitable facade system for your building. Curtain walls have more engineering requirements because they dominate the stunning glass-laden facade, while cladding panels are cheaper and provide better protection due to a wider variety of available materials. For professional guidance on choosing and installing facade systems, HSCS Decor is always ready to assist you as your reliable partner for exterior building solutions, Bar Systems Designs. Your Projects Our Past Experience Your Goals Are Professionally Met